Difference between revisions of "Xeno Fusion"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Megalomaniac (talk | contribs) |
Megalomaniac (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
'''proof of concept:''' haha, no proof to show yet, but initial testing promises good results | '''proof of concept:''' haha, no proof to show yet, but initial testing promises good results | ||
| − | == | + | ==Technical Data== |
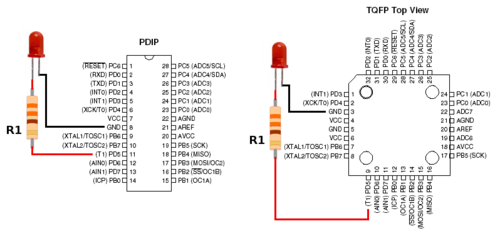
| + | The foundation for Xeno Fusion is based upon everyday simple LED connectivity.<br> | ||
| + | The diagram in figure 1 shows an LED connected to an Atmega8 (XenoGC) at pin PD5 and GND. Current flows from the anode to the cathode and a resistor is used for current limiting protection. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''fig. 1'''<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Xeno_fusion_example_LED.png|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Revision as of 23:28, 25 March 2013
....this page is under destruction

|
|---|
Main
concept: use a xenogc modchip in tandem with wiikey fusion drive replacement
theory: use the atmega 8 on the xenogc modchip to trigger a response required for the WKF to initialize iso loading.
proof of concept: haha, no proof to show yet, but initial testing promises good results
Technical Data
The foundation for Xeno Fusion is based upon everyday simple LED connectivity.
The diagram in figure 1 shows an LED connected to an Atmega8 (XenoGC) at pin PD5 and GND. Current flows from the anode to the cathode and a resistor is used for current limiting protection.
Circuit
add diagram and parts here
Glossary
| Confusing terms easily explained | |
|---|---|
| Reverse Voltage | maximum voltage that can be applied before it blows up |
| Forward Voltage | minimum voltage required to operate. (basically, it is safe to apply any voltage amount between "forward" and "reverse" ) |
| Forward Current | available amount of current after flowing thru the device (10$ - 7$ = 3$ available )(3$ = forward current)) |
| Operational Current | amount of current required by a device for normal operation (see forward current 7$) |
| Maximum (or continuous) Forward Current |
maximum current that can be applied before a device burns up ( |
| Current-Limiting Resistor | a resistor used to protect a device from receiving too much current (see maximum forward current) |
| Voltage Drop | the voltage a component uses to operate. (the voltage difference from the power supply and the amount of voltage used by a component) |
| Transistor | used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power. (two types of bipolar transistors: NPN or PNP) |
| Relay | electromechanical or solid state device used to provide a normally open or normally closed output when energized or de-energized |
| Diode | device which allows current to pass in one direction and blocks current in the opposite direction |
| Photodiode | device capable of converting light into either current or voltage (a solar cell is a photodiode) |
| Infrared LED | LED which outputs light in the infrared spectrum (see photodiode) |
| ADC | Analog to Digital Converter which can be used to measure voltage |