Xeno Fusion
....this page is under destruction

|
|---|
Main
concept: use a xenogc modchip in tandem with wiikey fusion drive replacement
theory: use the atmega 8 on the xenogc modchip to trigger a response required for the WKF to initialize iso loading.
proof of concept: haha, no proof to show yet, but initial testing promises good results
Technical Data
The foundation for Xeno Fusion is based upon basic LED connectivity.
The diagram in figure 1 shows an LED connected to an Atmega8 (XenoGC) at pin PD5 and GND. Current flows from the anode to the cathode and a resistor is used for current limiting protection.
fig. 1
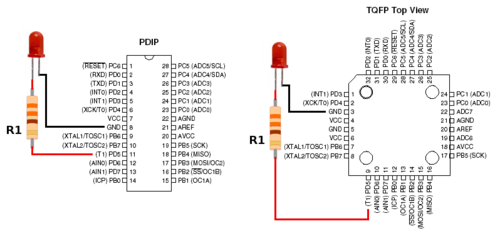
Atmega8L (XenoGC) operates at 3.3v and will deliver up to 3.3v @ 40mA output per pin.
If an LED is rated at 2.0v forward voltage with up to 20mA forward current, then a current-limiting resistor value of 220ohms will provide 5.9mA of operational current which is under 20mA of forward current allowing a safe operation condition for the LED. Also the current-limiting resistor creates a 1.3v voltage drop.
current = (( supply voltage - forward voltage ) / resistor value ) * 1000
current = (( 3.3v - 2v ) / 220 ohm) * 1000
current = (( 1.3v ) / 220ohm) * 1000
current = (( 0.0059 ) * 1000
current = 5.9 mA
voltage drop = resistance * current
voltage drop = 220ohm * 5.9 mA
voltage drop = ~ 1.3v
Circuit
add diagram and parts here
Glossary
| Confusing terms easily explained | |
|---|---|
| Reverse Voltage | maximum voltage that can be applied to a component before it blows up |
| Forward Voltage | minimum voltage required by a component for normal operation. (basically, it is safe to apply any voltage amount between "forward" and "reverse" ) |
| Maximum (or Continuous) Forward Current |
maximum current that can be continuously applied to a component before it burns up |
| Operational Current | any amount of current provided to a component which allows save operation (see Forward Current) |
| Current-Limiting Resistor | a resistor used to protect a component from receiving too much current (see Forward Current) |
| Max Peak Forward Current | maximum current that can be applied during a brief current spike. typically ignore this value and rely on the forward current the component can safely handle to determine the current limiting resistor value. |
| Voltage Drop | the voltage difference from the power source subtracted by the forward voltage equals the voltage used by the current limiting resistor. |
| Transistor | component used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power. (two types of bipolar transistors: NPN or PNP) |
| Relay | electromechanical or solid state device used to provide a normally open or normally closed output when energized or de-energized |
| Diode | component which allows current to pass in one direction and blocks current in the opposite direction |
| Infrared LED | Light Emitting Diode which outputs light in the infrared spectrum |
| optical isolator | component that transfers electrical signals between two isolated circuits by using light (see Infrared LED) |
| Photodiode | component capable of converting light into either current or voltage (example: a solar cell is a photodiode) |
| Photodiode opto-isolator | a device which consists of a photodiode paired with an LED. The LED provides a source of light, the photodiode detects the light and allows the flow of energy from an external source. non-mechanical equivalent of a relay. (see Relay) |
| ADC | Analog to Digital Converter which can be used to measure voltage |